What is MakerDAO, Governance, Current State and Tokenomics Explained
MakerDAO stands as one of the oldest decentralized finance protocols on Ethereum, operating since 2017. The protocol generates DAI, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar through overcollateralized lending. Users deposit crypto assets into smart contract vaults and mint DAI against their collateral. The system has generated approximately 8.4 billion DAI as of early 2026, with a market capitalization around 5.36 billion dollars. In August 2024, the protocol rebranded to Sky while maintaining backward compatibility with existing DAI and MKR tokens.
The protocol operates through a vault system where users lock collateral worth more than the DAI they generate. Each vault type requires specific collateralization ratios, typically between 150 and 200 percent. When ETH valued at 150 dollars sits in a vault, users can generate up to 100 DAI, maintaining the required overcollateralization. The protocol maintains stability through liquidation mechanisms that automatically sell collateral when positions become undercollateralized. Treasury bills now form the largest collateral category at 2.18 billion dollars, representing a shift toward real-world assets alongside traditional crypto holdings like ETH and WBTC.
How Does Someone Actually Use MakerDAO to Borrow Stablecoins?
Users access MakerDAO through platforms like Oasis Borrow or Sky.money, connecting via MetaMask or hardware wallets. The process begins by selecting a collateral type from supported assets including ETH, WBTC, stETH, and various other tokens. After depositing collateral into a vault, users specify how much DAI to generate while monitoring their collateralization ratio. The minimum DAI generation was historically 100 DAI, though requirements vary by vault type. Gas fees on Ethereum mainnet add to transaction costs, making vault creation and management more expensive during network congestion.
Borrowers pay stability fees that range from 1.5 to 8.75 percent annually depending on governance decisions and vault type. These fees compound continuously but are expressed as annual percentage rates. Users can repay borrowed DAI and reclaim collateral anytime without fixed schedules or minimum payments. If collateral value drops and the vault approaches its liquidation ratio, owners must either add more collateral, repay DAI, or face automatic liquidation with penalties typically around 13 percent. The system offers no credit checks or identity requirements, operating entirely through smart contracts that execute transparently on the blockchain.
What Makes MakerDAO Governance Different From Other DeFi Protocols?
MKR token holders control all protocol parameters through on-chain voting. These holders decide stability fees, debt ceilings, collateral types, liquidation ratios, and the DAI Savings Rate that pays interest to DAI holders. Voting power scales directly with MKR holdings, creating a plutocratic system where large holders wield disproportionate influence. Recent votes have shown concentration among roughly 20 entities controlling 80 percent of voting power, raising questions about true decentralization. The transition to SKY governance tokens in 2025 maintained this structure with a 1 to 24,000 conversion ratio from MKR.
The Endgame plan launched in 2024 introduces SubDAOs now called Stars, which operate as independent entities within the broader ecosystem. Spark Protocol became the first Star, managing its own lending operations while integrating with MakerDAO's core infrastructure. Each Star develops specialized functions, governance tokens, and business models. This modular approach aims to scale governance by delegating specific responsibilities while maintaining overall protocol cohesion. Critics argue the complexity adds governance overhead, while supporters see it as necessary evolution for managing diverse revenue streams including real-world asset integration that now generates approximately 19.4 million dollars in monthly revenue.
How Does MakerDAO Compare to Aave and Compound in 2026?
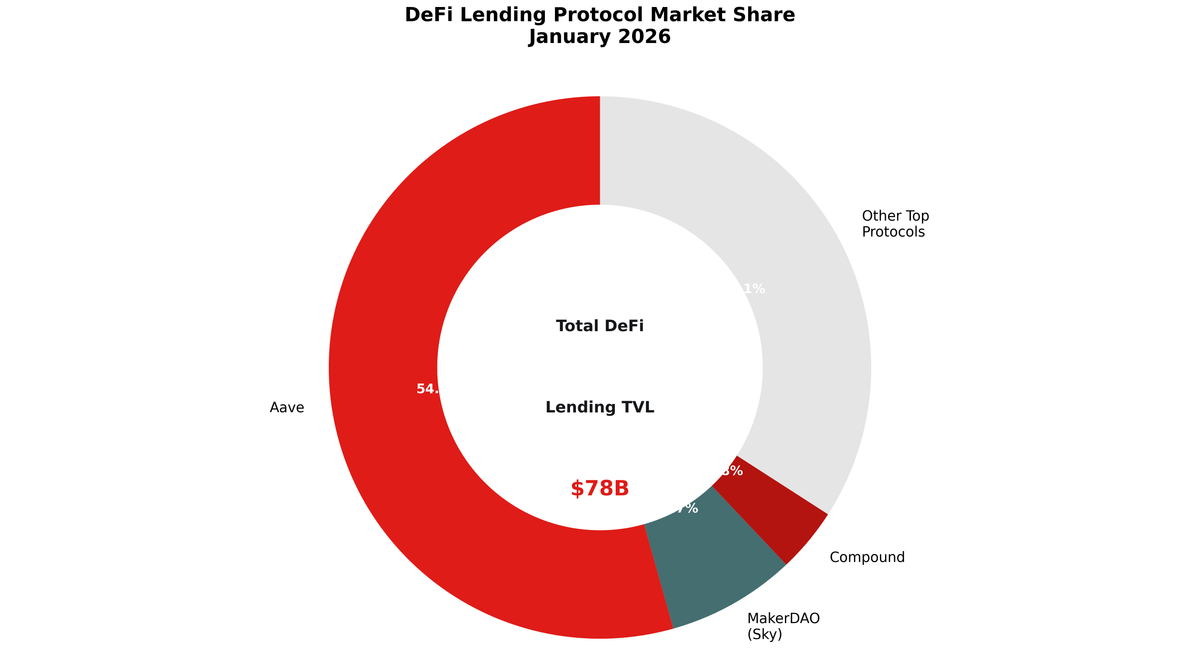
Aave dominates DeFi lending with roughly 42.4 billion dollars in total value locked across multiple chains, compared to MakerDAO's 6 billion and Compound's 3 billion. Aave offers variable and stable rate loans across dozens of assets on Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, and other networks. Its flash loan feature enables uncollateralized borrowing within single transactions, serving arbitrageurs and liquidators. Compound maintains a simpler model with algorithmic interest rates based purely on utilization, generating approximately 77 million in monthly fees despite zero protocol revenue since fee switches remain disabled by governance.
MakerDAO differs fundamentally by focusing on stablecoin generation rather than multi-asset lending pools. Users cannot deposit DAI to earn yield on MakerDAO itself; they must use the DAI Savings Rate or external platforms. The protocol excels at providing decentralized dollar exposure backed by diverse collateral including the largest real-world asset holdings in DeFi. Where Aave and Compound compete on asset breadth and cross-chain deployment, MakerDAO concentrates on maintaining DAI's peg and expanding collateral diversity. The comprehensive tooling ecosystem available to DAOs like MakerDAO enables sophisticated governance and treasury management absent from simpler lending protocols.
What Is the Current Financial State of MakerDAO in Early 2026?
The protocol holds approximately 6 billion dollars in total value locked with 948 million in real-world asset collateral representing 14 percent of reserves. Monthly fees reached 37 million dollars as of late 2025, with retained revenue around 19.4 million supporting operations and token buybacks. The DAI Savings Rate sits at 4.5 percent APY as of mid-2025, attracting 1.32 billion in deposits to the savings contract. Weekly peg volatility remains minimal at 0.003 percent, demonstrating effective stability mechanisms. The protocol ranks among the top three DeFi platforms by TVL, though it has ceded market share to Aave's multi-chain expansion.
MKR token trades around 1,520 dollars with a market cap near 1.93 billion as of January 2026. The token serves dual purposes as governance rights and recapitalization mechanism. When protocol revenue exceeds expenses, surplus gets used to buy and burn MKR, reducing supply. If collateral auctions fail to cover bad debt, new MKR gets minted and sold, diluting holders but restoring solvency. The Sky rebrand introduced USDS as an upgradeable version of DAI and SKY as the new governance token, though adoption has stalled with DAI supply actually growing 9 percent while USDS declined 10 percent through mid-2025. Only 4,656 wallets hold sUSDS earning the Sky Savings Rate, suggesting limited migration enthusiasm despite marketing efforts.
What Are the Risks and Future Outlook for MakerDAO?
Smart contract risk persists despite multiple audits and years of operation. The protocol's complexity spanning multiple contracts, oracles, and liquidation systems creates potential attack surfaces. Oracle failures could trigger mass liquidations or allow manipulation of collateral prices. The shift toward real-world assets introduces regulatory exposure as governments scrutinize stablecoin operations. The EU's MiCA regulation effective in 2026 requires transparency and reserve standards that may conflict with decentralized governance structures, though diversified collateral including government bonds may ease compliance.
Price predictions for MKR range from 2,800 dollars by late 2026 to potentially 12,000 dollars by 2030 if the protocol captures institutional demand for decentralized stablecoin infrastructure. The Endgame roadmap completion expected in 2027 promises greater modularity and efficiency, though execution remains uncertain. Competition intensifies as Aave launches its GHO stablecoin and other protocols expand into stablecoin issuance. MakerDAO's first-mover advantage and proven stability mechanisms provide defensibility, but the failed Sky rebrand reveals challenges in evolving established brands. The protocol must balance innovation with the conservative approach that made DAI trusted among the hundreds of DAOs and DeFi protocols that integrate it as base collateral.
Sources
- CoinLaw: MakerDAO Statistics 2025 Real-Time DeFi Insights (September 2025)
- Blockworks: One Year Into Sky, Adoption Lags Behind Vision (August 2025)
- The Block: MakerDAO Rebrands to Sky, DAI Stablecoin Optionally Upgradeable to USDS (August 2024)
- CoinDesk: MakerDAO Is Now Sky as $7B Crypto Lender Rolls Out New Stablecoin (August 2024)
- Lampros Tech: Top DeFi Protocols 2025 TVL, Fees, Yield and Adoption Insights (September 2025)
- CoinMarketCap: Latest Dai News - Future Outlook, Trends and Market Insights (December 2025)
- DL News: State of DeFi 2025 (December 2025)
- Marketcapof: Best DeFi Projects in 2026 Ranked by Market Cap and TVL (December 2025)
- CoinPedia: Maker Price Prediction 2024, 2025, 2026 to 2030 (December 2025)
- Amberdata: Comparing Lending Protocols Aave vs Compound vs MakerDAO (July 2025)
- MakerDAO Community Portal: Vaults Onboarding Guide
- Gemini Cryptopedia: MakerDAO's DAI and DeFi for Collateralized Loans





