Aragon OSx Tech Stack Explained
What is Aragon OSx
Aragon OSx is a modular smart contract framework launched in March 2023. The stack enables developers to build DAOs that can evolve without redeploying core contracts. As of December 2024, over 7,000 DAOs run on this infrastructure across seven blockchain networks.
The framework solves a problem: traditional DAO smart contracts lock organizations into fixed governance models. Changing voting mechanisms or adding new features requires migration to entirely new contracts. OSx separates governance logic into plugins that install and uninstall independently.
The stack runs on Ethereum mainnet, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, Peaq, and Celo. Developers access it through three NPM packages or through a no-code interface at app.aragon.org. The protocol undergoes regular security audits with the most recent Halborn assessment completed in February 2025.
<div class="section">
<h2>Core Architecture</h2>
<h3>DAO Contract</h3>
<p>The DAO contract holds assets and executes approved actions. It stores metadata including ENS names, logos, and descriptions per ERC-4824. The contract manages native currency, ERC-20 tokens, ERC-721 NFTs, and ERC-1155 assets.</p>
<p>The contract executes actions through an execute() function that accepts an Action[] array. This allows batch execution of multiple operations in a single transaction. Actions can transfer assets, call contract functions, or interact with external protocols.</p>
<h3>Permission Manager</h3>
<p>The Permission Manager lives inside the DAO contract. It controls which addresses can call specific functions. Permissions use a modifier pattern that checks authorization before function execution.</p>
<p>Developers set permissions with granular parameters. A plugin might have permission to execute actions under $10,000 automatically, while larger amounts require additional signatures. The system supports conditional permissions through custom condition contracts.</p>
<h3>Plugin System</h3>
<p>Plugins add functionality without modifying the DAO contract. Each plugin handles specific logic: token voting, multisig approval, or treasury management. Plugins request permissions during installation and release them upon uninstallation.</p>
<p>The plugin architecture uses three interfaces: IDAO for DAO interaction, IPlugin for plugin identification, and IPermissionCondition for custom permission logic. Developers extend abstract contracts like Plugin, PluginCloneable, or PluginUUPSUpgradeable.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>OSx Framework Contracts</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Contract</th>
<th>Purpose</th>
<th>Key Functions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>DAOFactory</td>
<td>Creates new DAO instances</td>
<td>Deploys DAO contracts, registers in DAORegistry, assigns ENS subdomains</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>DAORegistry</td>
<td>Tracks deployed DAOs</td>
<td>Maintains registry of all protocol DAOs, enables discovery</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>PluginRepoFactory</td>
<td>Creates plugin repositories</td>
<td>Deploys version-controlled plugin repos</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>PluginRepoRegistry</td>
<td>Tracks plugin repositories</td>
<td>Maintains registry of available plugins, enables browsing</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>PluginSetupProcessor</td>
<td>Installs/updates plugins</td>
<td>Handles plugin installation, updates, and removal with safety checks</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p class="source">Data: Aragon OSx GitHub documentation and smart contract source code</p>
<p>Framework contracts manage the lifecycle of DAOs and plugins. The factory pattern ensures consistent deployment across all instances. Registries provide onchain discovery of DAOs and available plugins.</p>
<p>The PluginSetupProcessor handles complex installation logic. It grants necessary permissions, configures plugin settings, and ensures atomic operations. If installation fails, the processor reverts all changes to maintain DAO integrity.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Available Plugins</h2>
<div class="chart-container" style="height: 500px;">
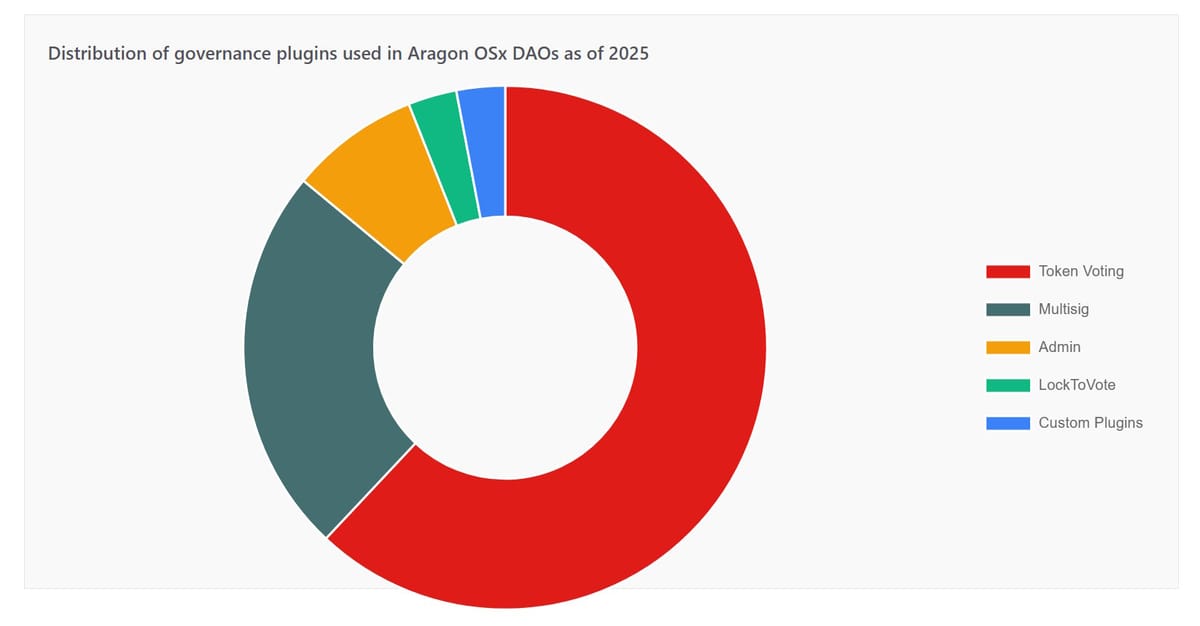
<div class="subtitle-chart">Distribution of governance plugins used in Aragon OSx DAOs as of 2025</div>
<canvas id="pluginChart"></canvas>
</div>
<p class="source">Data: Aragon ecosystem reports and GitHub plugin repositories, 2025</p>
<h3>Token Voting</h3>
<p>The most deployed plugin. Token holders vote proportionally to their balance. The plugin supports ERC-20Votes tokens with snapshot functionality. Proposals execute automatically after approval and timelock periods.</p>
<p>Parameters include minimum participation thresholds, support requirements, and voting duration. DAOs customize these settings through governance proposals. The plugin moved to its own repository in OSx v1.3.0 for independent versioning.</p>
<h3>Multisig</h3>
<p>Requires signatures from multiple addresses before execution. The plugin allows M-of-N configurations where M signers from N total members must approve. This pattern suits small teams or execution committees.</p>
<p>The multisig plugin operates independently or alongside voting systems. Common patterns use multisig for routine operations while token voting handles major decisions. The v1.4.0 update fixed NatSpec comments in the getProposal function.</p>
<h3>Admin</h3>
<p>Grants full execution permissions to a single address. Used for initial DAO setup or maintenance tasks. The admin can execute any action without voting or delays. This plugin should be removed after setup to prevent centralization.</p>
<h3>LockToVote</h3>
<p>Released in 2025 for Morpho Guardians V2. Token holders vote on multiple proposals simultaneously without balance snapshots. The plugin locks tokens during active voting periods to prevent double-voting across proposals.</p>
<h3>Custom Plugins</h3>
<p>Developers build custom plugins for specific use cases. Examples include DualTokenVoting by Unbound Labs, which combines soulbound tokens for core teams with transferable tokens for community members. The protocol supports unlimited custom implementations.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Plugin Development Process</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Step</th>
<th>Action</th>
<th>Requirements</th>
<th>Output</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1. Design</td>
<td>Define plugin logic and permissions needed</td>
<td>Understanding of DAO requirements</td>
<td>Technical specification</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2. Implement</td>
<td>Write smart contracts extending base plugin classes</td>
<td>Solidity knowledge, Hardhat setup</td>
<td>Plugin contract code</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>3. Test</td>
<td>Write comprehensive test coverage</td>
<td>Testing framework, test scenarios</td>
<td>Test suite with >80% coverage</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>4. Deploy</td>
<td>Deploy to target networks using factories</td>
<td>Network access, deployment gas</td>
<td>Deployed plugin contract</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>5. Publish</td>
<td>Create plugin repository with PluginRepoFactory</td>
<td>Metadata, version info</td>
<td>Discoverable plugin repo</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>6. Install</td>
<td>Use PluginSetupProcessor to install in DAOs</td>
<td>DAO permissions, setup parameters</td>
<td>Functional plugin in DAO</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p class="source">Data: Aragon developer documentation and plugin development guide</p>
<p>Plugin development requires no approval or API keys. Developers fork templates from GitHub, implement custom logic, and deploy permissionlessly. The Aragon team provides Foundry and Hardhat templates for quick starts.</p>
<p>Testing plugins locally uses Hardhat's network or testnets like Sepolia. The protocol-factory repository contains deployment scripts for multiple networks. Developers can test plugin installation on a local DAO before mainnet deployment.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Technical Stack Updates in 2025</h2>
<h3>EVM Address Integration</h3>
<p>The May 2025 update removed the restriction to OSx plugins only. DAOs now integrate any EVM-compatible address as a governing body. This allows Safe multisigs, OpenZeppelin Governor contracts, or external DAOs to participate in governance.</p>
<p>The integration works through the Permission Manager. DAOs grant specific permissions to external addresses just like plugins. A Safe multisig can receive veto rights while an external DAO approves budget allocations. The Aragon UI visualizes these relationships.</p>
<h3>Governance Designer</h3>
<p>Launched in May 2025, this tool creates complex governance flows without code. The Basic mode deploys single plugins like multisigs or token voting. The Advanced mode configures custom proposal types, stages, and roles.</p>
<p>The Staged Proposal Processor handles multi-step governance. Proposals can require initial screening, followed by token voting, then multisig execution. Each stage has independent parameters and permissions.</p>
<h3>Direct Smart Contract Upgrades</h3>
<p>Coming in late 2025, DAOs will upgrade OSx contracts through the Aragon App UI. Legacy DAOs built on v1.0.0 can access v1.4.0 features without developer intervention. The upgrade process runs through governance proposals for security.</p>
<p>This capability addresses technical debt in older deployments. DAOs receive new plugins, improved security features, and performance optimizations through standard proposal workflows. The upgrade maintains existing permissions and assets.</p>
<h3>Multichain Deployment</h3>
<p>OSx expanded to three networks in 2025. Peaq integration enables Machine Economy and DePIN governance. Celo supports mobile-first DeFi through the Value Accrual Toolkit. Optimism joined as part of Superchain expansion.</p>
<p>Cross-chain deployment uses identical smart contracts. A DAO on Arbitrum uses the same plugin code as Ethereum mainnet. Network-specific considerations include gas prices, block times, and available DEX liquidity for treasury management.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Gas Cost Analysis Across Networks</h2>
<div class="chart-container">
<div class="subtitle-chart">Average transaction costs for common Aragon OSx operations on supported networks in 2025</div>
<canvas id="gasChart"></canvas>
</div>
<p class="source">Data: Network documentation, L2Beat analytics, actual transaction data from 2025</p>
<p>Layer 2 networks reduce costs by 85-95% compared to Ethereum mainnet. Plugin installation that costs $180 on mainnet runs for $12 on Arbitrum. Token voting transactions drop from $22 to $2.</p>
<p>Network selection depends on DAO priorities. Ethereum mainnet offers maximum security and liquidity but highest costs. Arbitrum balances all factors well. Polygon provides lowest costs but less DeFi integration. Base attracts consumer applications with Coinbase backing.</p>
<p>Gas optimization in OSx contracts reduces baseline costs. The v1.4.0 release optimized storage patterns and removed unused code. Batch execution through Action[] arrays saves gas compared to individual transactions.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Security Audit History</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Version</th>
<th>Auditor</th>
<th>Period</th>
<th>Critical Issues</th>
<th>High Issues</th>
<th>Resolution</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>v1.4.0</td>
<td>Halborn</td>
<td>Nov 2024 - Feb 2025</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>N/A - Clean report</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>v1.3.0</td>
<td>Code4rena</td>
<td>Q2 2024</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>Fixed in v1.4.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>v1.3.0</td>
<td>Halborn</td>
<td>Q1 2024</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>N/A - Clean report</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>v1.0.0</td>
<td>Halborn</td>
<td>Q4 2023</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>0</td>
<td>N/A - Initial audit</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p class="source">Data: GitHub aragon/osx repository audit reports</p>
<p>Code4rena identified a potential reentrancy vector in the DAO executor in 2024. While rated medium severity, Aragon added reentrancy guards following best practices from OpenZeppelin Governor and Safe. The issue never led to actual exploits.</p>
<p>All audit reports appear publicly on GitHub. The Halborn v1.4.0 assessment is available at github.com/aragon/osx/blob/v1.4.0/audits/. Developers can review findings and verify resolutions before building on the stack.</p>
<p>No deployed Aragon OSx DAO has suffered a security exploit as of November 2025. The modular architecture limits blast radius. A vulnerable plugin affects only DAOs that installed it, not the entire protocol.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Real World Implementations</h2>
<div class="chart-container">
<div class="subtitle-chart">Major protocols using Aragon OSx tech stack and their assets under governance in 2025</div>
<canvas id="protocolChart"></canvas>
</div>
<p class="source">Data: Protocol websites, DeFi Llama, Aragon case studies</p>
<h3>Lido</h3>
<p>Lido runs Ethereum liquid staking governance on Aragon. The DAO controls node operator selection, protocol upgrades, and treasury allocation. Over $28 billion in staked ETH operates under this governance framework.</p>
<h3>Balancer</h3>
<p>Balancer uses OSx for protocol governance with $2.3 billion in liquidity. The DAO manages pool parameters, fee structures, and BAL token emissions. Token holders vote on protocol changes through the token voting plugin.</p>
<h3>Taiko</h3>
<p>Taiko deployed governance for its zkEVM rollup using OSx in 2025. The implementation prioritizes decentralization and security for protocol parameter updates. The DAO governs prover incentives and network upgrades.</p>
<h3>YieldNest</h3>
<p>YieldNest built custom governance using the Value Accrual Toolkit. The restaking protocol aligns token holder incentives with protocol growth. The implementation uses ve-style tokenomics with gauge voting for reward distribution.</p>
<h3>Geo Genesis</h3>
<p>Launched January 2025 as a knowledge governance platform. Each Space operates as an Aragon DAO with custom plugins for content curation. Editors vote on information quality using specialized governance mechanisms built on OSx.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Development Tools and Resources</h2>
<h3>Smart Contract Packages</h3>
<p>@aragon/osx contains Solidity source files for protocol contracts and interfaces. The package includes core contracts, plugin bases, and utility functions. Developers import these to build plugins or interact with deployed DAOs.</p>
<p>@aragon/osx-artifacts provides compiled bytecode and ABIs. This package allows interaction with deployed contracts without compiling from source. It includes addresses for all networks where OSx is deployed.</p>
<h3>Development Environment</h3>
<p>The protocol uses Hardhat for testing and deployment. Developers need Node.js 16 or higher. The workspace structure separates contracts, artifacts, and SDK into distinct packages.</p>
<p>Testing commands include `npx hardhat test` for full suite runs and `npx hardhat coverage` for code coverage reports. The team recommends >80% coverage before mainnet deployment.</p>
<h3>Documentation</h3>
<p>The developer portal at devs.aragon.org contains architecture guides, API references, and integration examples. The SDK documentation shows how to create DAOs, install plugins, and submit proposals programmatically.</p>
<p>GitHub contains plugin templates, deployment scripts, and example implementations. The Foundry template at aragon/osx-plugin-template-foundry provides a starting point for new plugins.</p>
<h3>Dune Analytics</h3>
<p>Public dashboards track OSx metrics. Developers can query DAO creation rates, plugin popularity, and transaction volumes. These dashboards use indexed blockchain data for real-time monitoring.</p>
<p>Additional DAO ecosystem resources are available in the <a href="https://daotimes.com/comprehensive-dao-tooling-guide-list-of-dao-tools/">comprehensive DAO tooling guide</a>. For exploring active DAOs, see the <a href="https://daotimes.com/a-comprehensive-list-of-daos-to-explore/">comprehensive DAO list</a>.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Frequently Asked Questions</h2>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">1. What programming language does Aragon OSx use?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">OSx smart contracts use Solidity. The core protocol and all official plugins are written in Solidity and compiled with Hardhat. Developers can also use Foundry for plugin development.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">2. How do plugins get permission to execute DAO actions?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">The DAO's Permission Manager grants specific permissions during plugin installation. Each plugin declares required permissions in its setup contract. The PluginSetupProcessor handles the grant process atomically.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">3. Can I upgrade my DAO without moving assets?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">Yes. The plugin architecture allows functionality changes without redeploying the core DAO contract. Assets remain in the same address. You install new plugins or update existing ones through governance proposals.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">4. What happens if a plugin has a bug?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">The DAO can revoke plugin permissions and uninstall it through a governance proposal. The modular design isolates issues to specific plugins. Core DAO assets and permissions remain protected even if a plugin fails.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">5. How does OSx handle plugin versioning?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">Each plugin lives in a PluginRepo contract that tracks versions using semantic versioning. DAOs can update to new plugin versions through the PluginSetupProcessor while maintaining their configuration and permissions.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">6. Can plugins interact with each other?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">Yes. Plugins can call functions in other plugins if they have appropriate permissions. Common patterns include a voting plugin that triggers a treasury plugin after proposal approval.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">7. What is the minimum viable DAO setup?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">A minimal DAO needs just the core DAO contract with at least one governance plugin. Many use the Admin plugin initially for setup, then install token voting or multisig plugins before removing admin access.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">8. How do I test plugins before mainnet deployment?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">Use Hardhat's local network or Ethereum testnets like Sepolia. The protocol-factory repository contains scripts for testnet deployment. Create a test DAO, install your plugin, and verify functionality before mainnet.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">9. Does OSx support non-transferable governance tokens?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">Yes through custom plugins. The DualTokenVoting plugin demonstrates this with soulbound tokens for core teams. Developers can create plugins that use any token standard including non-transferable implementations.</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">10. Where can I find deployed OSx contract addresses?</div>
<div class="faq-answer">The @aragon/osx-artifacts package contains addresses for all networks. Each deployment includes the DAOFactory, registries, and core plugins. The developer portal also lists addresses per network.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>Sources</h2>
<p><strong>Aragon Blog:</strong> Product Digest 001: May 2025 (June 2025)</p>
<p><strong>MetaLamp:</strong> Aragon DAO v2: Plugins, Permissions, and the New OSx Architecture (September 2025)</p>
<p><strong>Aragon Blog:</strong> Why Build your Custom DAO on Aragon OSx (August 2023)</p>
<p><strong>The Eagle Newsletter:</strong> The Modularity Behind Aragon OSx DAOs (October 2023)</p>
<p><strong>GitHub:</strong> Aragon OSx Protocol releases and documentation</p>
<p><strong>Aragon Developer Portal:</strong> Core architecture documentation</p>
<p><strong>Aragon Resource Library:</strong> Building a DAO Framework: Interview with Aragon CTO</p>
<p><strong>AppDeveloperMagazine:</strong> Aragon OSx app launches on Arbitrum (December 2024)</p>
</div>
Embedded JavaScriptEmbedded JavaScript

